Survivorship Bias
Your progress on this bias test won't be saved after you close your browser.
Understanding Survivorship Bias
Survivorship Bias
The tendency to focus only on people or things that succeeded, while ignoring those that failed and are no longer visible, leading to distorted conclusions.
What It Is
Survivorship bias happens when we draw conclusions based only on the examples that made it through a process, while ignoring those that did not. This leads to skewed perceptions, flawed strategies, and overestimated chances of success because the failures — often more numerous and instructive — are hidden from view.
Why It Happens
The bias arises because failures tend to be less visible. Successful cases are more likely to be documented, celebrated, or remembered, while unsuccessful ones are forgotten, discarded, or never reported. This incomplete data gives the illusion of higher success rates and better odds than actually exist.
People also tend to focus on success stories because they are more inspiring and emotionally satisfying. As a result, they overlook the more common — and often more instructive — cases where the same strategy, decision, or behavior led to failure.
Everyday Impact
Survivorship bias can affect personal judgment, business decisions, and even historical narratives:
In career planning, people may believe that dropping out of college leads to success because they see stories of tech billionaires who did just that. What they do not see are the countless others who dropped out and struggled.
In investing, individuals often study only the companies that succeeded and ignore the ones that failed, leading them to adopt risky strategies based on incomplete data.
In fitness, entrepreneurs, and creative industries, this bias creates unrealistic standards. We hear about the few who “made it” but rarely hear from the many who did everything right and still didn’t succeed.
The Cost of Ignoring the Whole Picture
When decisions are based only on visible outcomes, people overestimate the effectiveness of certain actions or strategies. They may pursue paths that look more promising than they are, or adopt beliefs that seem validated only because failures have been filtered out.
Recognizing what is missing — not just what is present — is key to making more balanced and realistic choices.
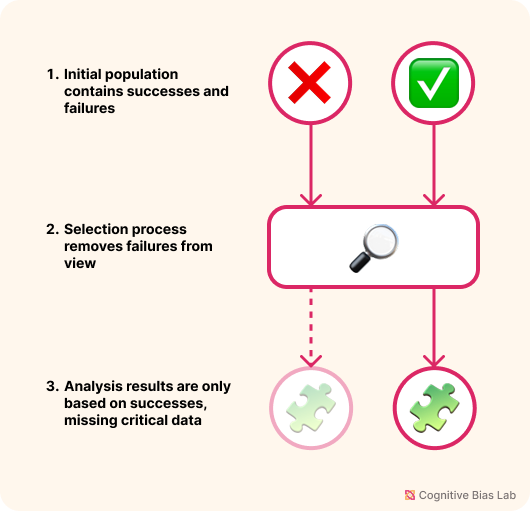
Visual representation of Survivorship Bias (click to enlarge)
Examples of Survivorship Bias
Here are some real-world examples that demonstrate how this bias affects our thinking:
Psychological Study Simulation
Experience a famous World War II study that revolutionized aircraft protection and revealed a crucial insight about data analysis. You'll examine damage patterns on bomber aircraft and discover how a counterintuitive solution saved many lives.
Customer Service Survey Bias
A company wants to measure customer satisfaction, so they send surveys to people who made a purchase. The results show overwhelmingly positive feedback, leading the company to believe their service is excellent. However, they failed to survey potential customers who never completed a purchase—possibly because of poor service. By only analyzing those who bought something, they miss critical data and make flawed conclusions about their overall service quality.
Startup Success Illusion
Entrepreneurs often read about the few startups that became billion-dollar companies, believing that following their strategies will lead to success. However, they rarely hear about the countless failed startups that followed the same paths but disappeared. Ignoring these failures creates an illusion that success is more common than it actually is.
The Myth of College Dropouts
We often hear stories of successful college dropouts like Steve Jobs and Mark Zuckerberg, leading many to believe dropping out increases the chance of success. However, this ignores the vast majority of dropouts who did not achieve similar success. The unseen failures distort our perception of reality.
How to Overcome Survivorship Bias
Here are strategies to help you recognize and overcome this bias:
Seek Out the Missing Data
Actively look for cases that didn’t succeed. Understanding why they failed provides a more realistic perspective on success rates.
Consider Base Rates
Use statistical data to understand the true likelihood of success, rather than focusing only on examples of those who made it.
Beware of Cherry-Picked Success Stories
When reading success stories, ask yourself: 'What happened to everyone else who tried the same thing?'
Test Your Understanding
Challenge yourself with these questions to see how well you understand this cognitive bias:
A consultancy firm is analyzing the effectiveness of a new marketing strategy. They focus on companies that successfully increased sales after implementing the strategy. What is the flaw in their approach?
Academic References
- Wald, A. (1943). A Method of Estimating Plane Vulnerability Based on Damage of Survivors.
- Rao, T. (2024, June 1). Understanding Survivorship Bias: Implications for Research and Decision-Making.
- Brown, Stephen J, and others, 'Survivorship Bias in Performance Studies', The Equity Risk Premium Essays and Explorations (New York, NY, 2006; online edn, Oxford Academic, 31 Oct. 2023)